Intersectional Analysis of Exposure to Programming Languages Reveals the Additive Impact of Belonging to Multiple Underrepresented Populations
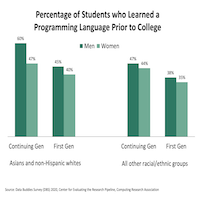
The current analysis examines whether exposure to programming languages varies among different populations that are underrepresented in computing, and whether belonging to multiple underrepresented populations is associated with programming experience. Results show that students from multiple underrepresented populations in computing are less likely to have learned a programming language than their peers.